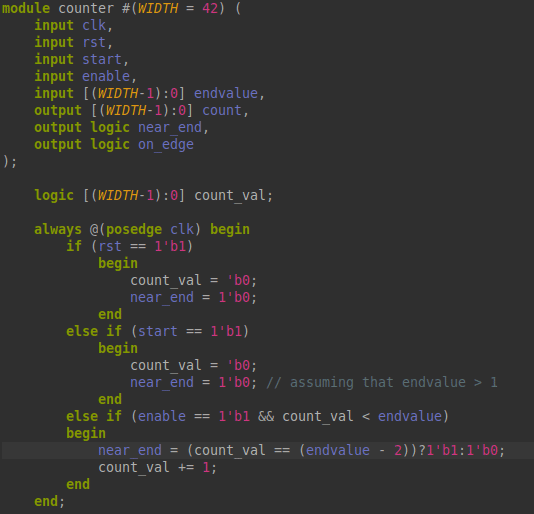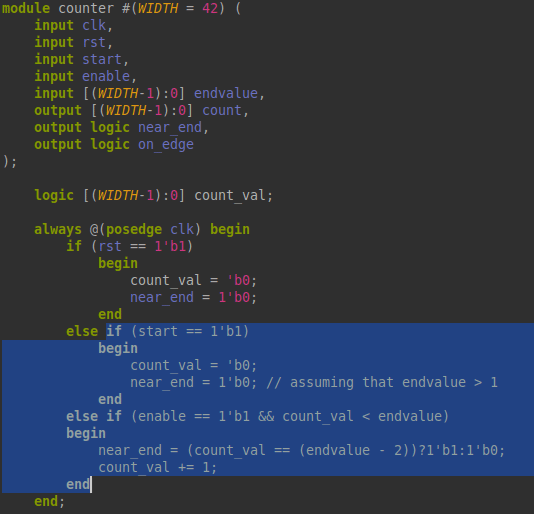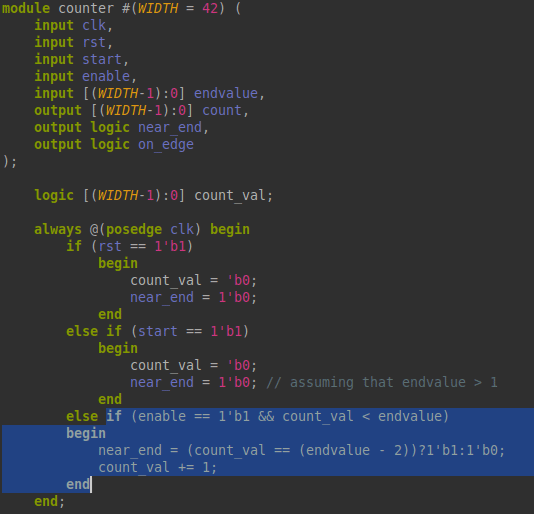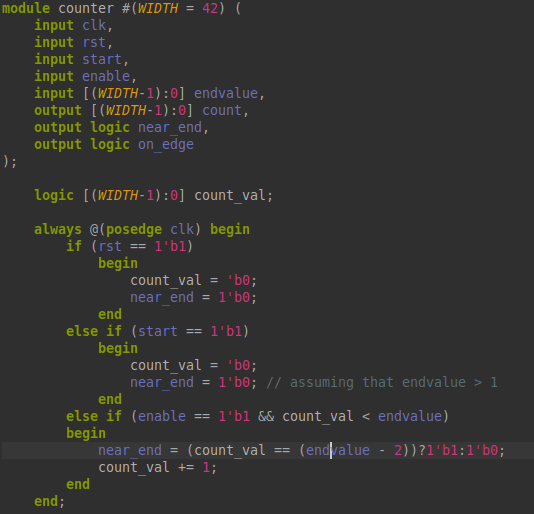
The Editor shows the content of files and allows you to edit files. It is a tabbed view such that multiple files can be opened simultaneously. The active file is the one currently selected.
VHDL and SystemVerilog Editor
The VHDL and SystemVerilog (or Verilog) editors are optimized to help you browse and edit VHDL and SystemVerilog code. Most browsing and editing features are similar for both languages.
Language-specific features are explained in “VHDL Specific” and “Verilog and SystemVerilog Specific”.
Code Highlighting (Syntax Coloring)
Sigasi Visual HDL (SVH) colors your code to make the structure more clear. Unlike other tools, SVH offers coloring based on the meaning of a word, rather than just the syntax.
SVH supports both syntax highlighting and semantic highlighting. Syntax highlighting colors pieces of code according to the lexical class the code belongs to, such as a keyword or string. Semantic highlighting colors code according to its meaning. For example, a constant is shown in another color than a signal.
Code highlighting is fully configurable for a number of VHDL and Verilog and SystemVerilog syntax and semantic elements. Also, Color, background, style, and font can be customized. Learn more about configuring colors.
Rather than configuring every color yourself, you might want to have a look at the supported Light and Dark themes. To switch between themes, go to Window > Preferences > General > Appearance where you can choose a theme. While it is possible to install additional themes, only the Light and Dark themes are supported by Sigasi.
Type-time Syntax Error Reporting
SVH marks VHDL and SystemVerilog syntax errors while you type. It will also report broken SystemVerilog preprocessor code.
Project Exploration and Navigation
SVH offers powerful techniques to explore a file or project and navigate through it. This section covers: Occurrence Highlighting, Find References, Open Declaration, and Hovering.
Occurrence Highlighting
If you click on an identifier, it will be highlighted, as well as all other occurrences of the identifier that refer to the same object. Note that this occurrence highlighting is intelligent: it is not based on the identifier’s string value, but on the object that the identifier refers to.
You can turn occurrence highlighting on or off. Click the “Toggle Mark Occurrences” icon ![]() in the toolbar.
in the toolbar.
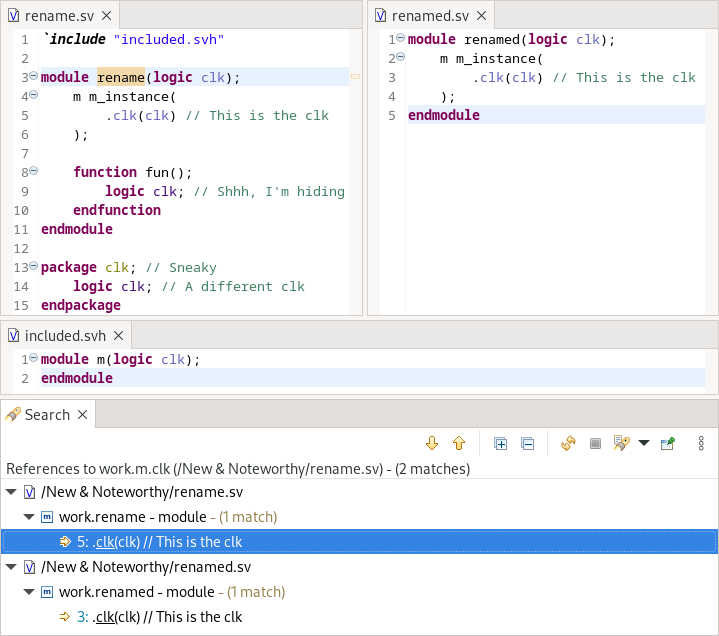
Find References
To look for occurrences of a given identifier in different files, place your cursor on the identifier and right-click. Now select Search References.
A search window will appear on the bottom of your workbench, displaying all occurrences of the selected identifier. You can easily navigate through all occurrences by clicking the Show Next Match arrow ![]() and the Show Previous Match arrow
and the Show Previous Match arrow ![]() in the search result view. Note that all occurrences are highlighted and marked with a small arrow at the left border of the editor for easy recognition.
in the search result view. Note that all occurrences are highlighted and marked with a small arrow at the left border of the editor for easy recognition.
Open Declaration and Hyperlinks
Open Declaration You can easily navigate to the declaration of any port, signal, entity, etc. Place the cursor on the identifier, right-click, and select Open Declaration. The editor immediately switches to the line that declares the object. Since this operation is so commonly used, it is assigned to the shortcut key F3.
Hyperlinks You can also navigate your code like a web browser by clicking hyperlinks. If you press and hold the Ctrl key, hyperlinks will appear in your editor. If you click the link (while holding the Ctrl key), you will navigate to the target of the link. SVH offers the following links:
- Link to Declaration: this has the same behavior as Open Declaration (F3)
- Link to Matching Entity [VHDL]: this links a component declaration of an instantiation to the matching entity declaration. This also works for component generics and ports (Shift+F3)
- Link to Matching Module [MIXED]: this links a component declaration of an instantiation to the matching Verilog module declaration. This also works for component generics and ports (Shift+F3). Modules that are instantiated as entity instantiations are also supported (
label : entity work.verilogmodule port map (...);) - Link to Matching Architecture for entity declarations [VHDL]
- Link to Matching When Clause [VHDL]: in finite state machines (FSMs) you can jump directly to the matching when part of your case statement from state transitions (Shift+F3)
- Link to Open Declaration in Package Body [VHDL]: in packages you can jump directly to the matching declaration in the package body (Shift+F3). This also works in the opposite direction, Open Declaration in Package Body
- Link to Open Declaration in Protected Type Body [VHDL]: in protected types you can jump directly to the matching declaration in the protected type body. This also works in the opposite direction, Open Declaration in Protected Type
- Link to Include files in SystemVerilog sources (F3)
- Link to Macro definition in SystemVerilog sources
- URLs in comments
Hover
To learn more about the declaration of a given identifier, hold your mouse pointer over it. After a short time, a popup shows you the name and datatype of the signal. This technique is called hovering.
The hover pop-up can show different kinds of information:
- datatype
- comments: inline documentation written at the declaration (association rules)
- value: the value of constants
- errors or warnings: a message, if the given identifier has an error or warning associated with it
- binary/decimal conversion: for hexadecimal, octal, or binary values, the decimal equivalent
Since Sigasi Studio 4.1 the hovers also offer extra links that make it easy to navigate to the declaration, find references, etc.
Autocomplete and Content Assist
SVH provides powerful autocompletion capabilities. This means that the tool can help you to complete identifiers and constructs as you are working on the code. Like other tools, the tool provides autocompletion based on the HDL language. However, it goes much further. It also provides autocompletion based on the design context. It can provide this additional level of intelligence as it knows all objects that have been declared in the design.
Autocompletion Interface
Autocompletion may come from different sources, as will be discussed in the following sections. However, the user interface to initiate them is always the same. At any point, as you are entering code, you can press Ctrl+Space and the tool will suggest appropriate autocompletion.
Based on the Design Context
SVH uses its knowledge of the design to provide intelligent autocompletion that boosts your productivity tremendously.
The tool knows which objects are appropriate and which identifiers are visible at any given point in the code. As you start typing and ask for autocompletion, it will suggest the appropriate identifiers as autocompletion candidates.
SVH provides help to autocomplete:
- component declarations
- component instantiations
- entity instantiations
- module instantiations
- case statements (based on variables/signals with an enumeration type)
- SystemVerilog preprocessor/macro directives (
`define,`ifndef, …) - SystemVerilog include paths (
`include "): triggering autocomplete between the double quotes will present a list of files and folders. If you select a folder, trigger autocomplete again to get completions in this folder.
Based on Templates
SVH can help you to declare VHDL and SystemVerilog objects, using autocompletion based on templates. SVH comes preconfigured with templates for all common declarations and statements, including (for VHDL):
- function, procedure
- process
- type: enum, file, range, array, record
- signal, constant, variable
- component
- entity
- architecture
- entity/architecture pair
- package/package body pair
- and much more
Some autocompletions are templates that require further user input. In such a case, the editor goes into a special template editing mode after the autocompletion has been performed. You can use TAB to cycle through the items that have to be modified or completed. When done, you can press ENTER to return to the normal editing mode. The cursor will be placed at an appropriate position to continue working.
You can also configure your own templates. To edit or create templates, go to Window > Preferences > Sigasi > VHDL or Verilog/SystemVerilog > Templates. Here you get an overview of existing templates. You can create New… templates, Edit… existing templates, or remove templates.
In the template editor, you can type ${ and press Ctrl+Space to see a list of the available variables.
Templates can be exported and imported. This is useful for sharing templates with colleagues.
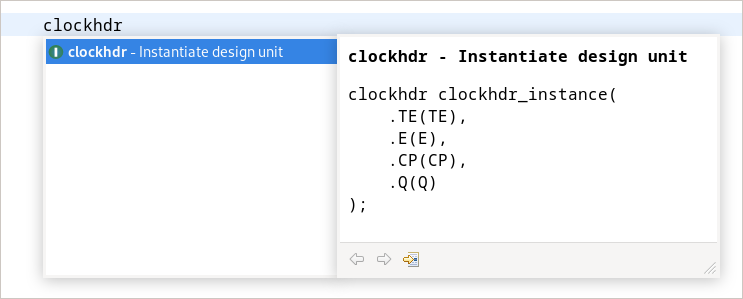
Instantiating a Design Unit
Note: In other tools, this feature may be known as paste as instantiation or port translation.
SVH knows all design units (entities, components, and modules) in the design and their port and parameter or generic interface, and can therefore automate much of the instantiation process. At the point in the code where you normally enter the design unit’s name, you can use autocompletion instead to suggest a list of possible design units. Upon selection, the tool will complete the instantiation with a generic or parameter list, and a port list with named associations. As an initial suggestion, each actual parameter will have the same name as its formal parameter. Of course, the actual parameter names need to be reviewed and edited by the user. Therefore, the editor will go into template editing mode after the autocompletion.
Note that design units will only be shown if they are visible in the current scope.
A number of VHDL-specific and Verilog and SystemVerilog-specific autocompletes are available in SVH.
Code Formatting
Automated consistent code formatting makes code more readable and helps developers understand code, whether working on their own code or when cooperating with colleagues.
Read more about specifics on VHDL code formatting and Verilog and SystemVerilog code formatting.
Formatting Configuration
You can set preferences for tabs or spaces under Window > Preferences > General > Editors > Text Editors.
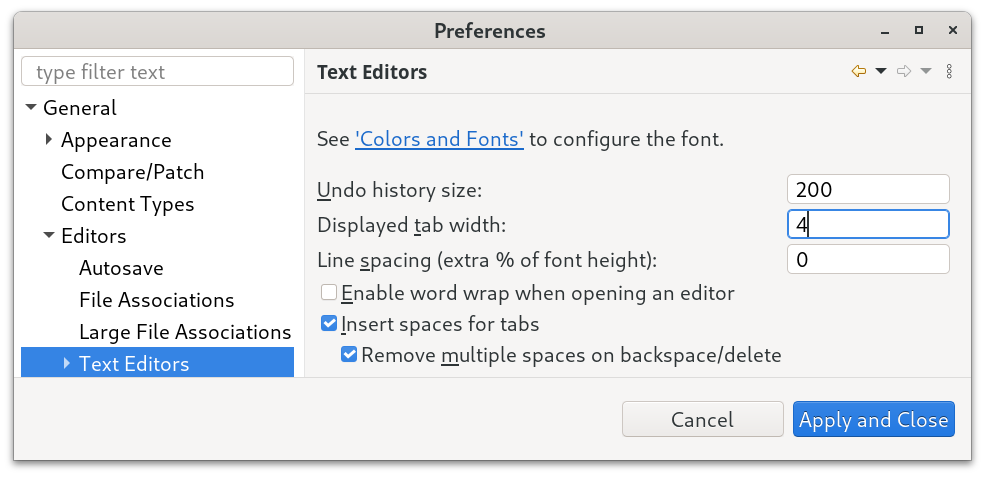
Here you can set the tab width in spaces and configure to Insert Spaces for Tabs. Whenever a tab is pressed, the corresponding number of spaces will be inserted instead. You can also opt to Remove multiple spaces on backspace/delete so that removing leading spaces follows the indentation levels.
Format Code on Save
You can configure SVH to automatically format your (System)Verilog and VHDL files when you save your source files via Window > Preferences > Sigasi > [VHDL | Verilog/SystemVerilog], next check Enable code format on save.
Format Files Without Opening Them
[Only in Sigasi Visual HDL Professional Edition]
You can format (System)Verilog and VHDL files without opening them in the editor.
You can format an entire project. Right-click the project in the Project Explorer and select Source > Format. Note that only files that are part of the build will be formatted.
You can format a selection of files. Select multiple files and/or folders in the Project Explorer and select Source > Format. Any selected file, part of the build or not, will be formatted. Any combination of resources can be formatted this way: multiple projects at a time, a project and a folder …
Other Editor Features
Code Folding
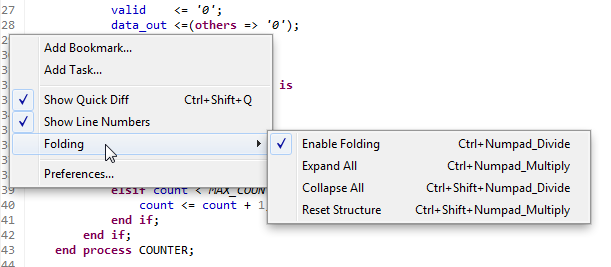
If you work with large files, you might want to hide certain pieces of your code. This can be done with code folding. Certain constructs, such as if-statements or process-statements can be folded so that they use a single line in the editor view. You can do this by clicking the little "-" symbol next to the statement.
You can also enable/disable code folding and perform other actions by right-clicking in the gutter (the small column to the left of your code) and selecting Folding.
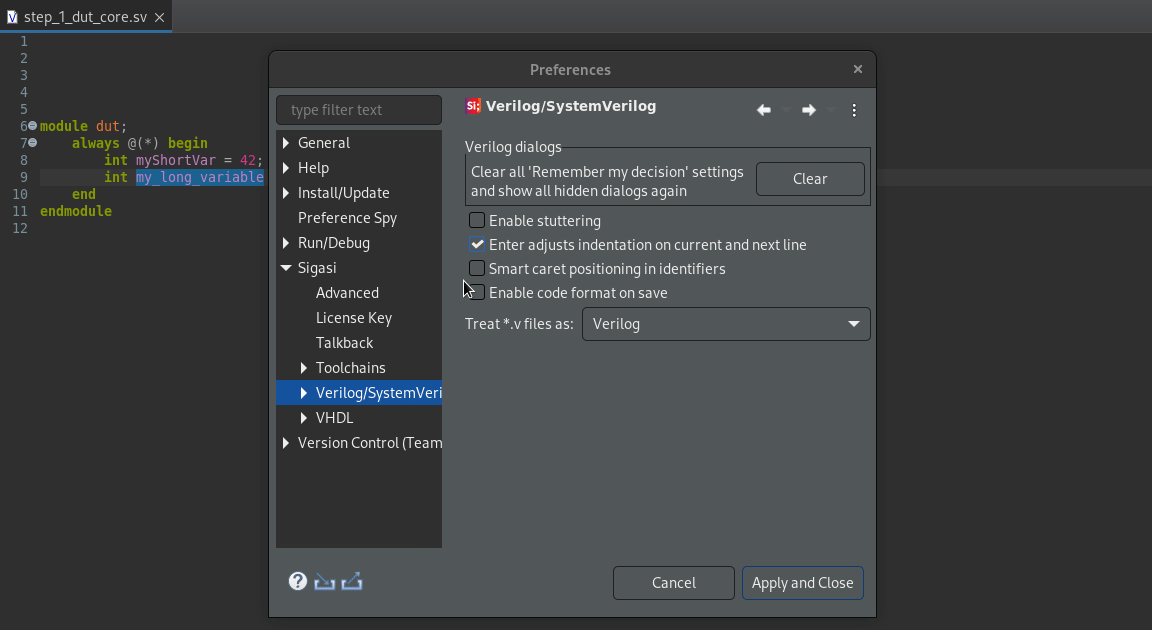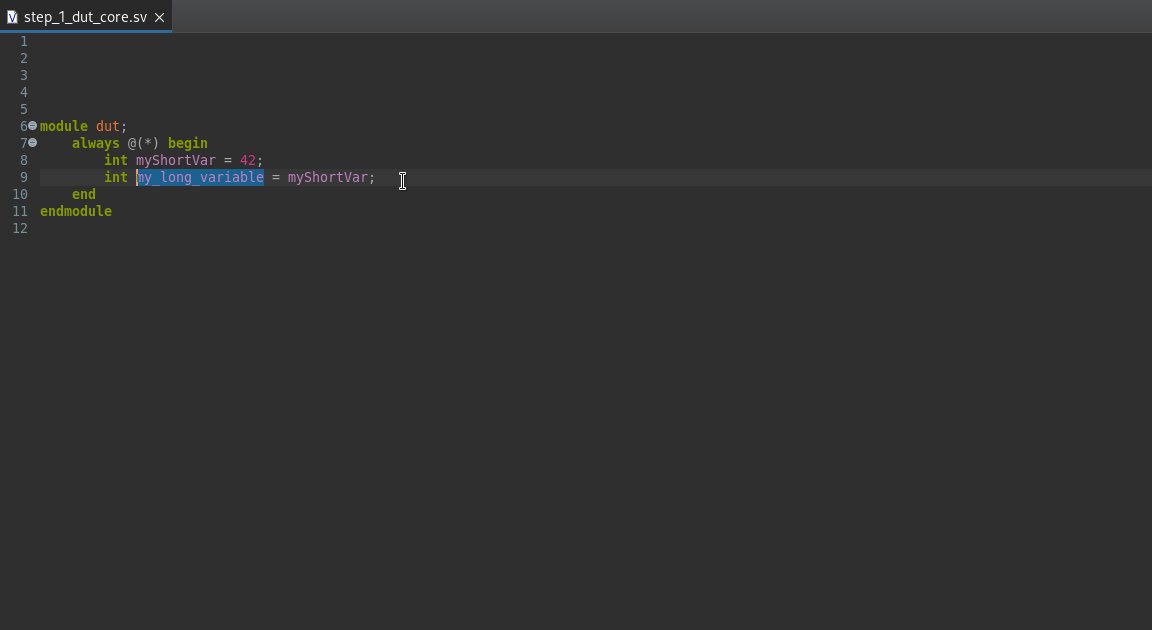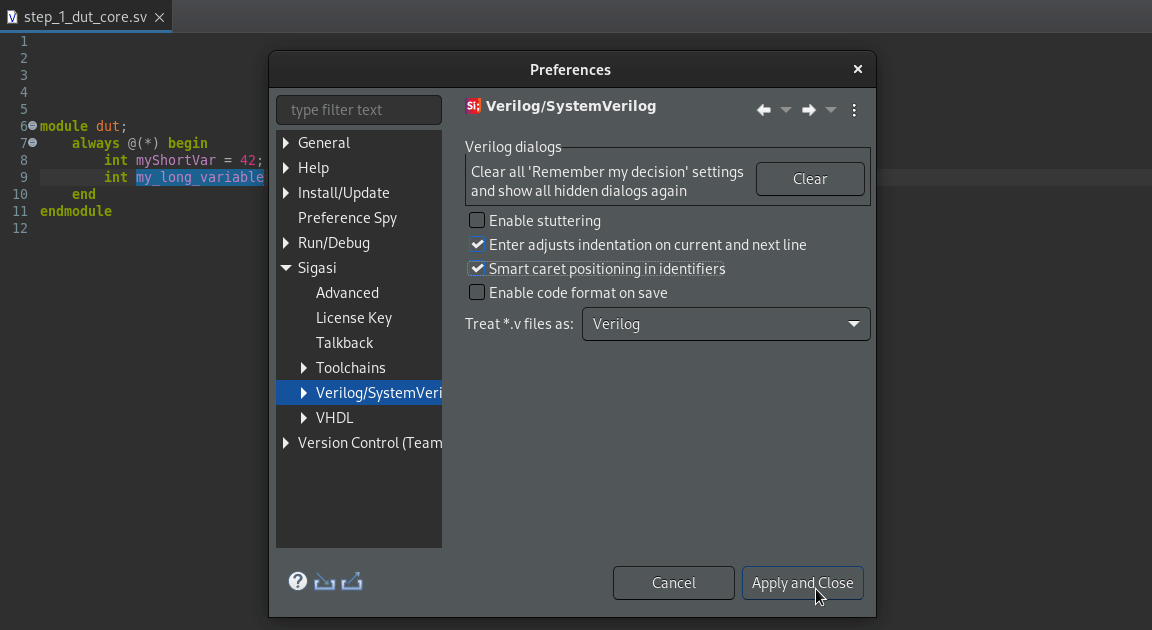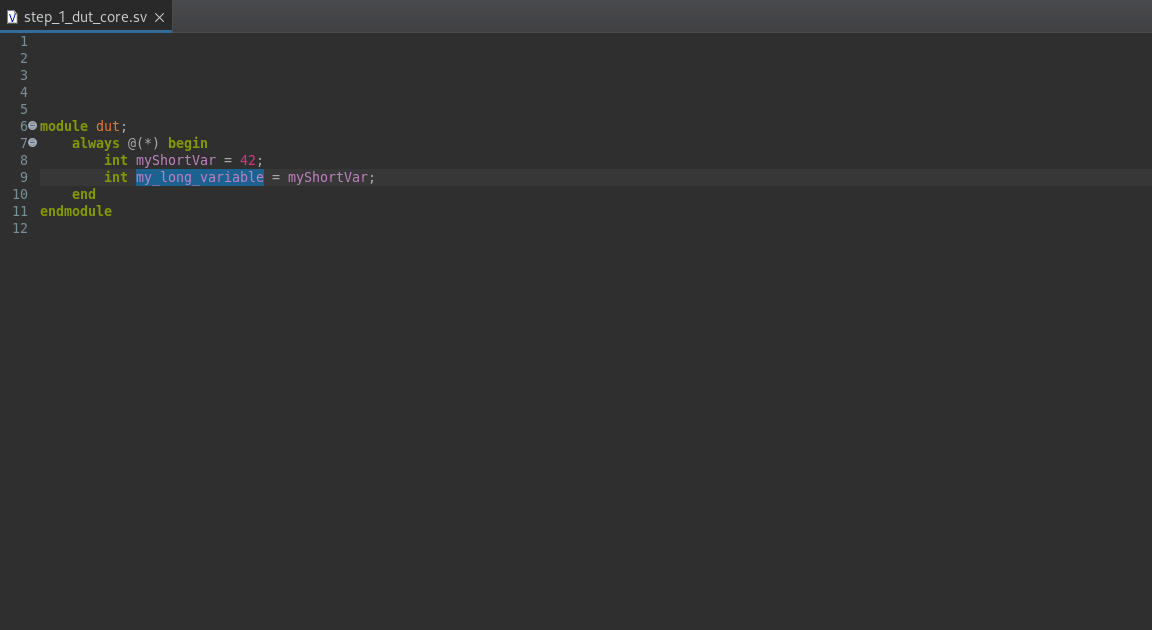
Smart Caret Positioning
Smart caret positioning allows you to easily jump between words within identifiers, no matter whether you use camelCase or snake_case, by using Ctrl+Left arrow and Ctrl+Right arrow.
Sigasi Studio 4.15 added the option to disable smart caret positioning in identifiers, both in VHDL and (System)Verilog. To change the setting, go to Window > Preferences > Verilog/SystemVerilog or Window > Preferences > VHDL where you can alter the selection of Smart caret positioning in identifiers.
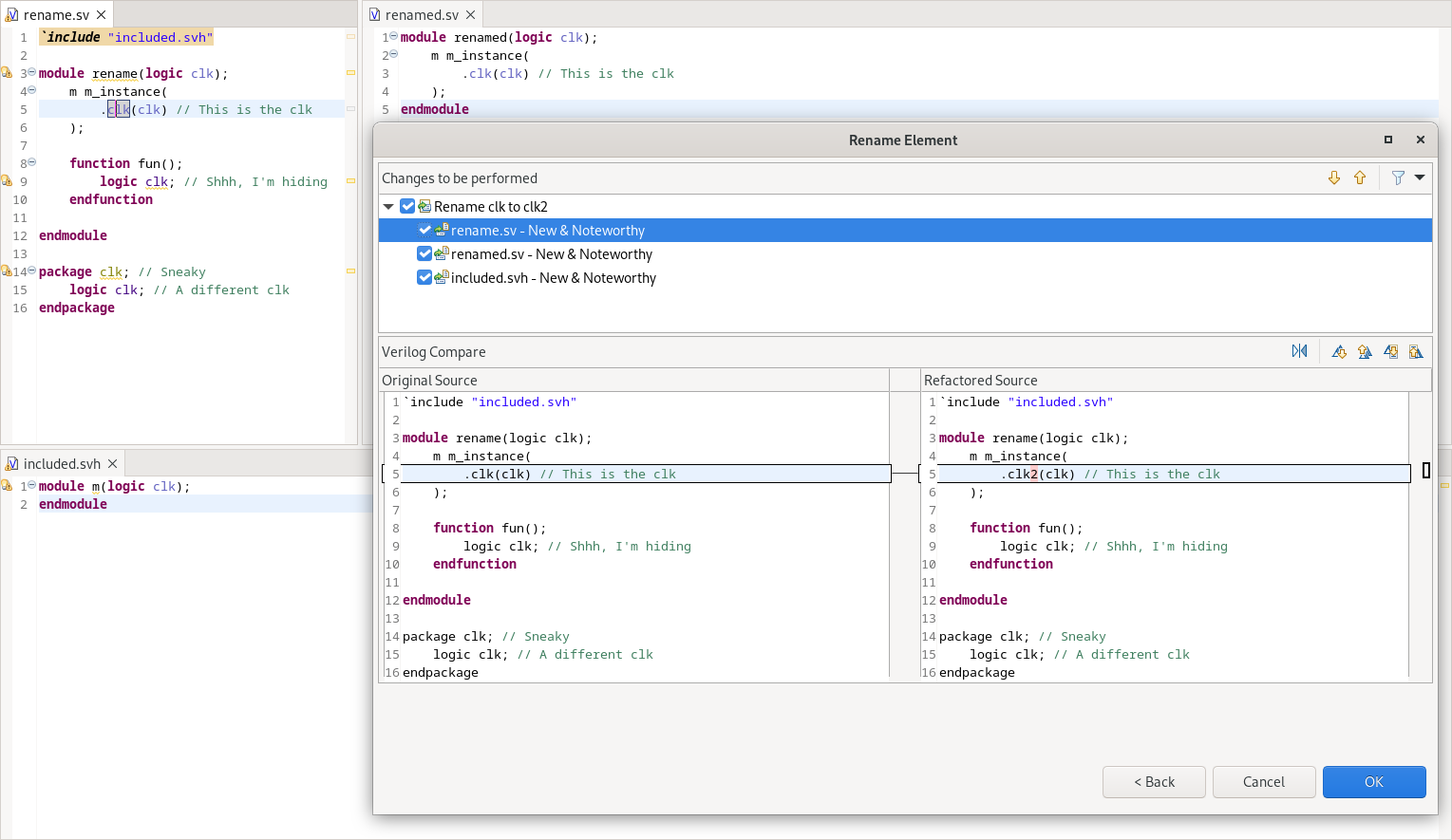
Rename Refactoring
Right-click on any identifier (VHDL or SystemVerilog) and select Refactor > Rename element (Alt+Shift+R) to change the name of the declaration and all its references. If you press Alt+Shift+R twice, you can preview the rename before applying it.
Full-screen View
Double-click on the editor tab to make it full-screen. You can also use Ctrl+M to achieve the same.
Block Selection
Note: In other tools, this feature may be known as column editing or column select.
Block selection is an alternative to standard (paragraph) selection. Block selection mode differs from standard selection mode in that it allows to select rectangular regions, or to set the cursor over multiple lines. Block selection is ideal for selecting vertical regions, for example, a column of a table or all port names in a port map.
To toggle between normal and block selection modes use Alt+Shift+A or press the Toggle Block Selection icon in the toolbar.
Structured Selection
Structured Select enables you to select VHDL or SystemVerilog code, based on its syntactic structure.
Screencast: Select code, based on its structure
- Shift+Alt+Up, expands the selection to the smallest syntax element that contains the current selection. You can then further expand the selection by invoking the action again.
- Shift+Alt+Down, contracts the current selection to the nested syntax expression that still contains the current cursor position. You can then further contract the selection by invoking the action again.
- Shift+Alt+Left, adds the syntax element left of the current selection to the selection. You can then further expand the selection by invoking the action again. You can also expand the selection in the other direction with Shift+Alt+Right
Add Parentheses or Create a String
When you select a region and press ( or [, the selected region is enclosed with the matching closing parentheses, ) or ].
When you select some text and press ", the selected text will be transformed into a string.
This works for both regular and multi-line strings.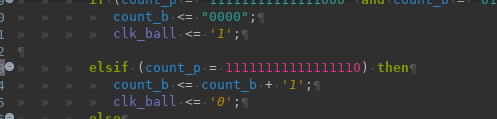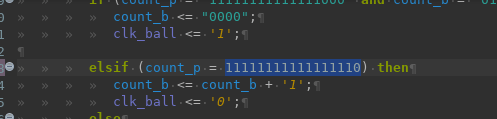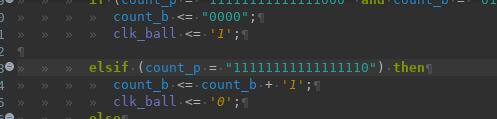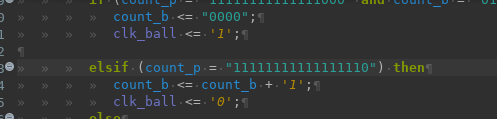
This behavior can be disabled by unchecking Enclose selected region when typing parentheses or quotes in Window > Preferences > Sigasi > VHDL.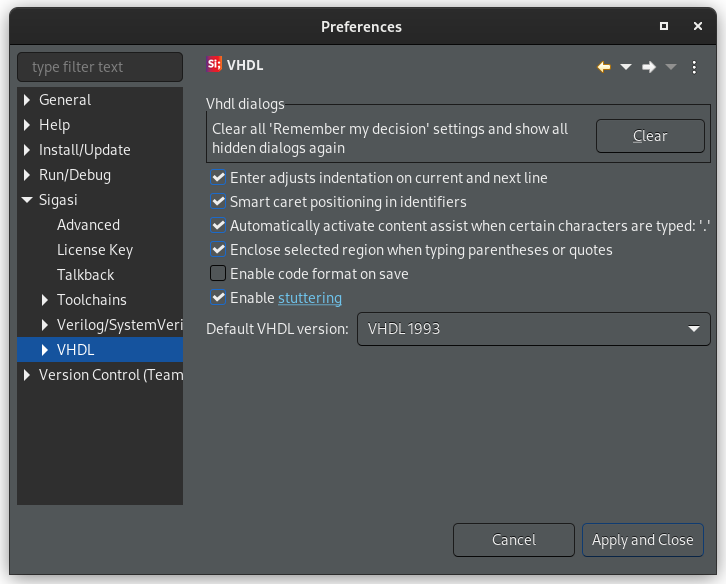
Show Whitespace
You can turn show or hide whitespace markers by clicking the Show Whitespace Characters icon ![]() in the toolbar.
in the toolbar.
Move and Duplicate Lines
You can easily move lines up and down by pressing: Alt+Up and Alt+Down.
You can duplicate your current line, or the lines of the current selection by pressing: Ctrl+Alt+Down.
Configure Key Bindings
Emacs/VI Emulation Mode
See VI and Emacs
Remove Trailing Whitespace
The action to remove trailing whitespace is hidden by default. You can access it by pressing Ctrl+3, typing RTW, and then selecting the correct action. Alternatively, you can bind this action to Keyboard Shortcuts of your preference. This action is being executed on the saved file, not in the editor. So before using this action, you have to make sure your file is saved.
Customize Color Preferences
There are several ways to customize color preferences in SVH.
- Choose the Eclipse Theme in the Window > Preferences > General > Appearance preferences menu.
- Edit Eclipse Colors and Fonts setting in the Colors and Fonts sub-menu.
- Change color setting for different text editor features in Window > Preferences > General > Editors > Text Editors
- Annotation colors can be configured in the Annotations sub-menu.
- Highlighting colors for differences can be configured in the Quick Diff sub-menu.
- Syntax coloring for Verilog/SystemVerilog can be changed in the Window > Preferences > Sigasi > Verilog/SystemVerilog > Syntax Coloring preferences menu.
- Syntax coloring for VHDL can be changed in the Window > Preferences > Sigasi > VHDL > Syntax Coloring preferences menu.
Multiple Screen Support
You can right-click the title tab of any view and select Detach to move the view into a separate window that can be dragged to another screen. Alternatively, you can drag a view out of the current window to create a new window from it.
Once multiple windows are available, views can be dragged between screens.
Resetting the SVH perspective will move all views into a single window.
See also this FAQ item.
Split Editor
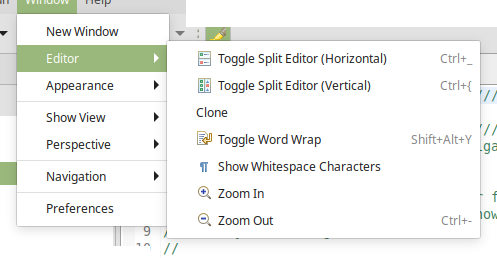
The Editor View can be split or duplicated in independent viewports that access the same file buffer. There are 3 ways to split the Editor View.
 Horizontal Split shows 2 viewports on top of each other.
Horizontal Split shows 2 viewports on top of each other. Vertical Split shows 2 viewports next to each other.
Vertical Split shows 2 viewports next to each other.- Clone to a new Editor View. This new Editor View can be detached so that the same file buffer can be viewed on multiple displays.
To split the editor view, go to Window > Editor and select the desired action.
There are Keyboard Shortcuts
to toggle the Horizontal Split (Ctrl+_) and the Vertical Split (Ctrl+{).
There can only be a single horizontal or vertical split within an Editor View. Multiple Editor Views can be cloned and re-arranged to obtain a custom layout with many views on the same file buffer.
Side-by-side Diff
- Previous versions (local history or version control)
- Comparing two files
Opening Project Files
The default way to open files in the VHDL and SystemVerilog editor is to double-click the files in the Project Explorer. But there are more methods to open files in your projects.
Open Resource
When you press Ctrl+Shift+R the Open Resource dialog opens. In this dialog, you can type a name or pattern to open a specific file name.
Open Design Unit
When you press Ctrl+Shift+D the Open Design Unit dialog opens. In this dialog, you can search in the list of VHDL, Verilog, or SystemVerilog design units and rapidly open the design unit you’re looking for.
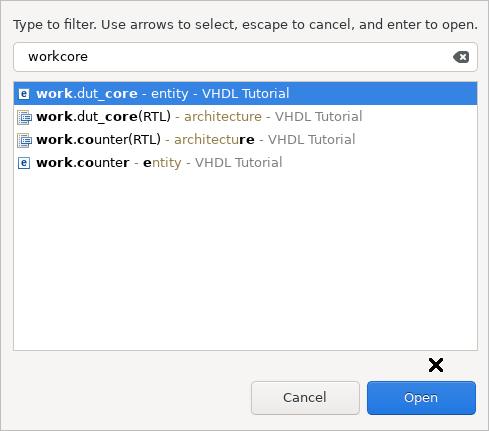
While typing, the corresponding matching characters in the design unit descriptions are highlighted. You might notice how the design units are not ordered alphabetically, but instead by best match.
Hint: there’s no need to bother writing special characters and upper case letters in the search field. Our search filter will find your design unit without them. It looks for consecutive matches in the design unit descriptions, prioritizing those with longer and earlier matches. Moreover, it offers smart case search: lower case letters match both lower case and upper case letters, but you can narrow down the search by using upper case letters, those only match themselves.
Note that excluded design files do not appear in this list.
VHDL Specific
In addition to the powerful features of an Eclipse editor, the VHDL editor that comes with SVH supports a number of advanced editing features that are specifically useful for VHDL editing. These are described in this chapter.
Code Highlighting
Highlighting Classes for VHDL:
- Syntax : Comment, Keyword, Number, String, Task tag
- Semantic : Constant, Port, Signal, Type, Variable, Attribute, Function/Procedure, Labels
VHDL Specific Autocompletes
Declaring a Component
Note: In other tools, this feature may be known as paste as component or port translation.
If you want to use instantiation based on a component (as opposed to direct instantiation) you need to associate an entity with a component. SVH can automatically declare a component for an existing entity. At the point where you normally enter the component name, you can use autocompletion instead to show the list of available entities. Upon selection, the tool will automatically complete the component declaration.
Type Conversion
In VHDL design you need to do a lot of type conversions. SVH’s
autocomplete functionality can help you with those. Put a dot (.)
after the element you want to convert, and the autocomplete suggestions
will appear. The conversion functions have descriptions like convert type and convert to ...
Smart Indentation
When you press enter, SVH automatically adjusts the indentation of
the current and the new line. Depending on the content of the preceding
line, SVH will automatically increase or decrease the indentation
level. E.g. an extra indent after an if-statement and removal of an
indent for the matching else-clause.
You can enable/disable this feature via Window > Preferences > Sigasi > VHDL by toggling the Enter adjusts indentation on current and next line setting.
Tabs vs. spaces: This feature inserts tabs characters or spaces, according to your preferences.
See also:
- Tabs and Spaces
- Screencast Smart Indent for VHDL
VHDL Code Formatting
Press Ctrl+Shift+F to format your current VHDL file.
This includes:
- indentation
- spacing between keywords and references
- vertical alignment of certain symbols like `<=``
Context-based
SVH’s formatter is context-based and tries to respect the author’s style. So depending on your source style, the formatter might make different choices.
One example is the decision to format a conditional signal assignment on one, or multiple lines. SVH makes this decision based on the position of the first else keyword. If you put the else keyword on the first line, the formatter will put everything on one line. If you put the else keyword on a new line, the formatter will use multiple lines for the assignment.
demo <= (others => '0') when enable = '1'
else (others => '1') when input = '1' -- else on new line
else (others => 'X');
Note about broken code: If your VHDL source file contains syntactical errors, the formatter cannot always figure out appropriate formatting. For this reason, the formatter is programmed to stop applying (whitespace) changes beyond unsupported syntax errors.
Configuration
You can set your preferences for tabs or spaces under Window > Preferences > General > Editors > Text Editors.
VHDL-specific code formatting can be configured at Window > Preferences > Sigasi > VHDL > Formatting:
- Preserve newlines: this option configures the formatter to not add or remove any newlines in your code.
- Vertical alignment: this option configures the formatter to vertically align consecutive declarations and statements for example on
<=or:. - Lowercase/Uppercase keywords: when this option is set to
UPPERCASEthe formatter will convert all VHDL keywords to uppercase. When this option is set tolowercase, the keywords will be converted to lowercase. When this option is set toignore, the case of keywords won’t be changed by the formatter.
Note: A Sigasi Visual HDL Designer Edition license is required for this option. - Alignment column for trailing comments: this setting configures what column SVH aligns trailing comments to. The default is 40, you can choose -1 to not align trailing comments.
Correct Indentation Only
SVH can also correct the indentation of your code without making any other changes. Inside a VHDL editor, open the context menu and click Source > Correct Indentation, or hit Ctrl+I. This only changes whitespace at the start of your lines.
If you select code first, only the code in the selection will be indented.
Disable Formatting in Defined Regions
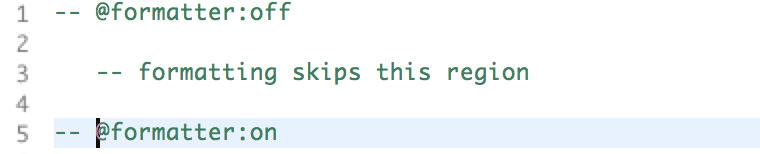
You can disable the formatter for defined regions in your VHDL source files by add off and on tags:
- off tag:
-- @formatter:off- Turns of the formatter until an on tag is encountered
- on tag:
-- @formatter:on- Reenables the formatter following an off tag
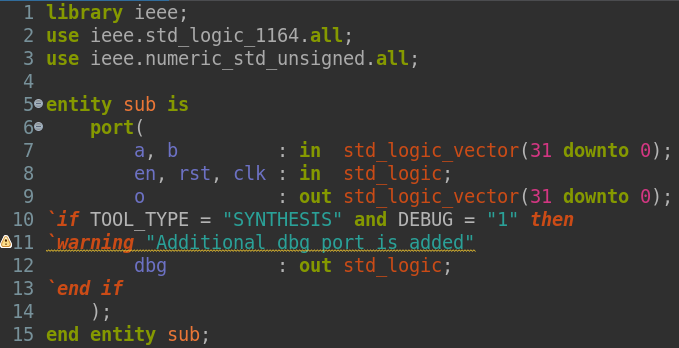
VHDL 2019 Tool Directives
Sigasi Studio 4.16 introduced VHDL 2019 tool directives, which are a simplified version of the preprocessor found in SystemVerilog or the C family of languages.
Tool directives allow to conditionally enable code based on tool type, debug mode, or really any other custom variable.
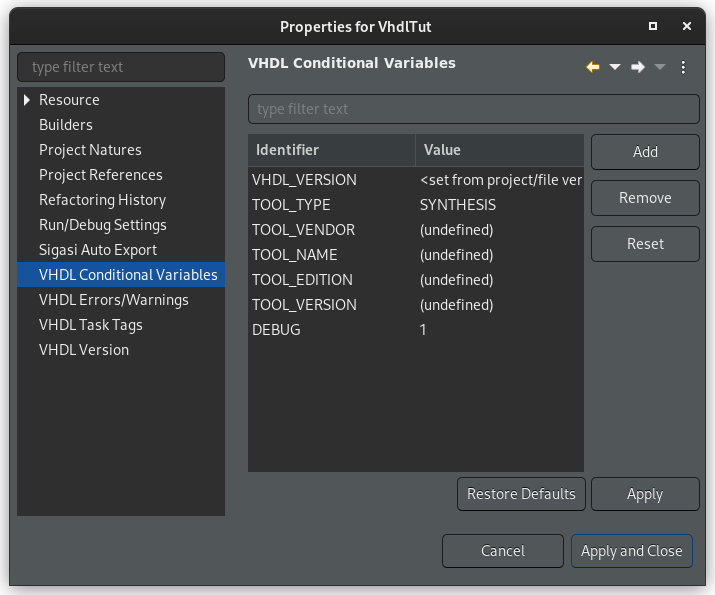
You can edit the defined tool directives by right-clicking your project and then going to Properties > VHDL Conditional Variables.
Check out the video to see directives in action.
Stuttering
Stuttering is an editing technique popularized by Emacs, that lets you
type certain things really fast. You activate it by tapping a certain
key twice which will expand it to something more complex. For example, press
the period key . twice, and the editor will expand it to a right
arrow =>. Stuttering works like double-clicking: if you type keys
slowly, the stuttering mechanism will not be triggered.
The following stuttering keys are available:
| Keys | Effect |
|---|---|
| ,, | <= |
| .. | => |
| ;; | := |
Stuttering is enabled by default but can be toggled through the Enable stuttering option in the Window > Preferences > Sigasi > VHDL menu.
Verilog and SystemVerilog Specific
In addition to the powerful features of an Eclipse editor, the Verilog and SystemVerilog editor that comes with SVH supports a number of advanced editing features that are specifically useful for SystemVerilog editing. These are described in this chapter. Currently, Verilog 2005 (IEEE 1364-2005) and SystemVerilog 2017 (IEEE 1800-2017) are supported.
Code Highlighting
Highlighting Classes for Verilog and SystemVerilog:
- Syntax : Comment, Keyword, Number, String, Task tag, Operator
- Semantic : Assignment, Class, Covergroup, Macro, Enum, Function, Localparam, Module, Net/Wire, Parameter, Port, Type
Verilog and SystemVerilog Specific Autocompletes
Inserting an Include File
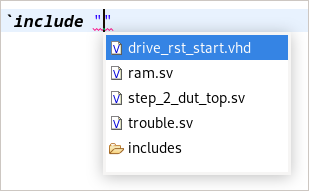
Making a typo in the file name of an `include causes swarms of errors. To prevent this, you can just press Ctrl+Space
between the double quotes of the include directive. You’ll be presented with all the files visible from
your current include path.
Smart Indentation
When you press enter, SVH automatically adjusts the indentation of
the current and the new line. Depending on the content of the preceding
line, SVH will automatically increase or decrease the indentation
level. E.g. an extra indent after a module and the removal of an indent for
the matching endmodule.
You can enable/disable this feature via Window > Preferences > Sigasi > Verilog/SystemVerilog by toggling the Enter adjusts indentation on current and next line setting.
Tabs vs. spaces: This feature inserts tabs characters or spaces, according to your preferences.
See also:
- Tabs and Spaces
- Screencast Smart Indentation for Verilog
Verilog and SystemVerilog Code Formatting
Press Ctrl+Shift+F to format your current Verilog or SystemVerilog file.
The default formatter implementation corrects indentation only.
Since Sigasi Studio 4.15, Sigasi ships with Verible built-in. Verible is an ambitious SystemVerilog formatter that is agnostic to macro invocations and includes and therefore produces a consistent formatting result even in heavily preprocessed code.
You can enable the Verible formatter for your installation by going to Window > Preferences > Sigasi > Verilog/SystemVerilog > Formatting. Under Select formatter, you can choose between the default Sigasi formatter which corrects indentation, and using the Verible formatter.
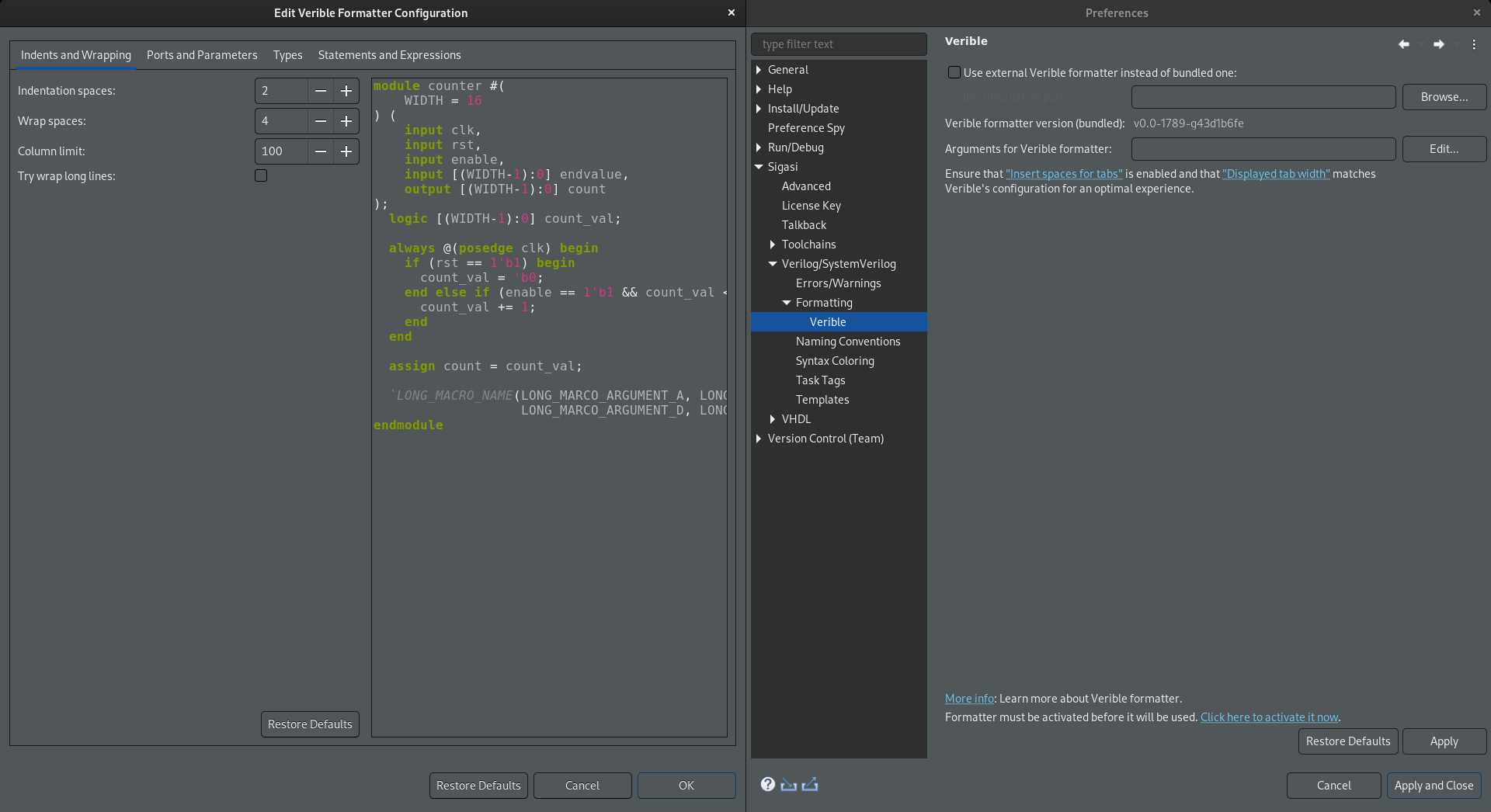
Sigasi ships with a recent Verible version by default. If you’d rather run your own Verible installation, this can be achieved in Window > Preferences > Sigasi > Verilog/SystemVerilog > Formatting > Verible. To select your own Verible binary instead of the one that comes with Sigasi, select the Use external Verible formatter instead of bundled one: option and configure the Verible installation path: option.
This page also allows you to customize the Verible formatting rules, both for the built-in and the external Verible binaries, by pressing the Edit… button. For maximal compatibility, you need to make sure the Eclipse setting to Insert spaces for tabs is enabled and that the Displayed tab width is matching the Verible configuration.
In the Verible configuration page, configurations are grouped in the following tabs.
- Indents and Wrapping
- Ports and Parameters
- Types
- Statements and Expressions
If you want to undo your changes, you can use the Restore Defaults button, either per tab or for the entire dialog. After applying your configuration changes, press the OK button.
To see this in action, you can have a look at our screencast.
The Verible website and README contain more information.
Verilog Version
You can configure the Verilog version via Window > Preferences > Sigasi > Verilog/SystemVerilog
and select whether *.v files are treated as Verilog (IEEE 1364-2005) or SystemVerilog (IEEE 1800-2017). *.sv files are always treated as SystemVerilog.
Include Paths and Initial Preprocessor Definitions
Sigasi attempts to resolve missing Include Paths automatically. However, it is highly recommended that the include paths be explicitly configured to ensure the include path order is accurate.
There are several ways to add include paths. A Quick Fix is available on `include warnings
in the editor which will automatically add the missing include path. Include paths can also be added through the
Add to Include Paths context menu item in the Project Explorer.
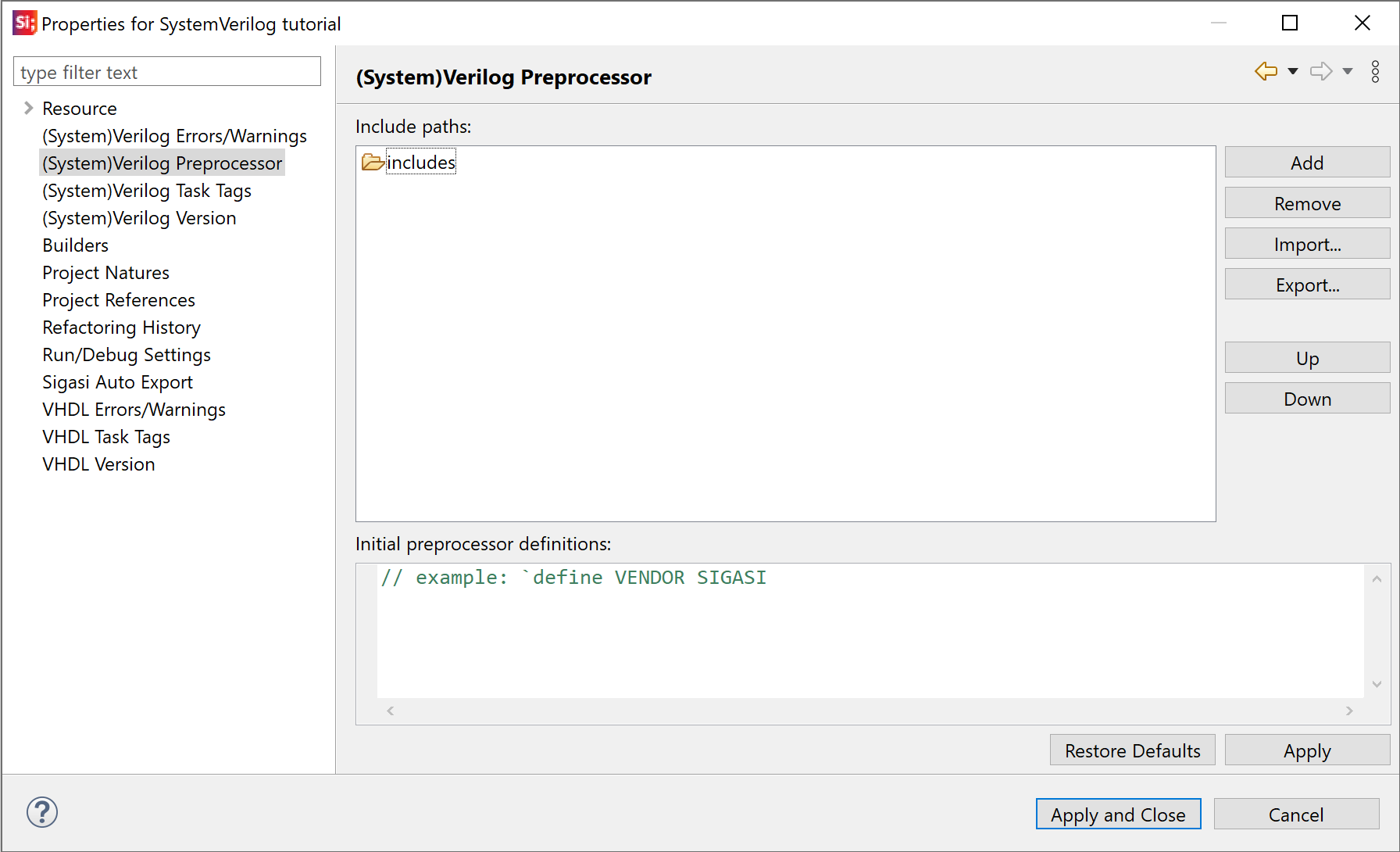
You can configure the include paths in the Verilog Preprocessor property page as well.
Right-click your project and select Properties > Verilog Preprocessor.
Here you can Add and Remove include paths using the buttons on the right.
You can also move the order of the include paths using the Up and Down buttons.
The Import... and Export... buttons can be used to transfer a semicolon-separated (;) list of include paths from and to the clipboard.
In the Initial preprocessor definitions field, you can configure definitions that are set before other files in the project are processed.
This allows you to, for example, set global defines without an explicit include statement.
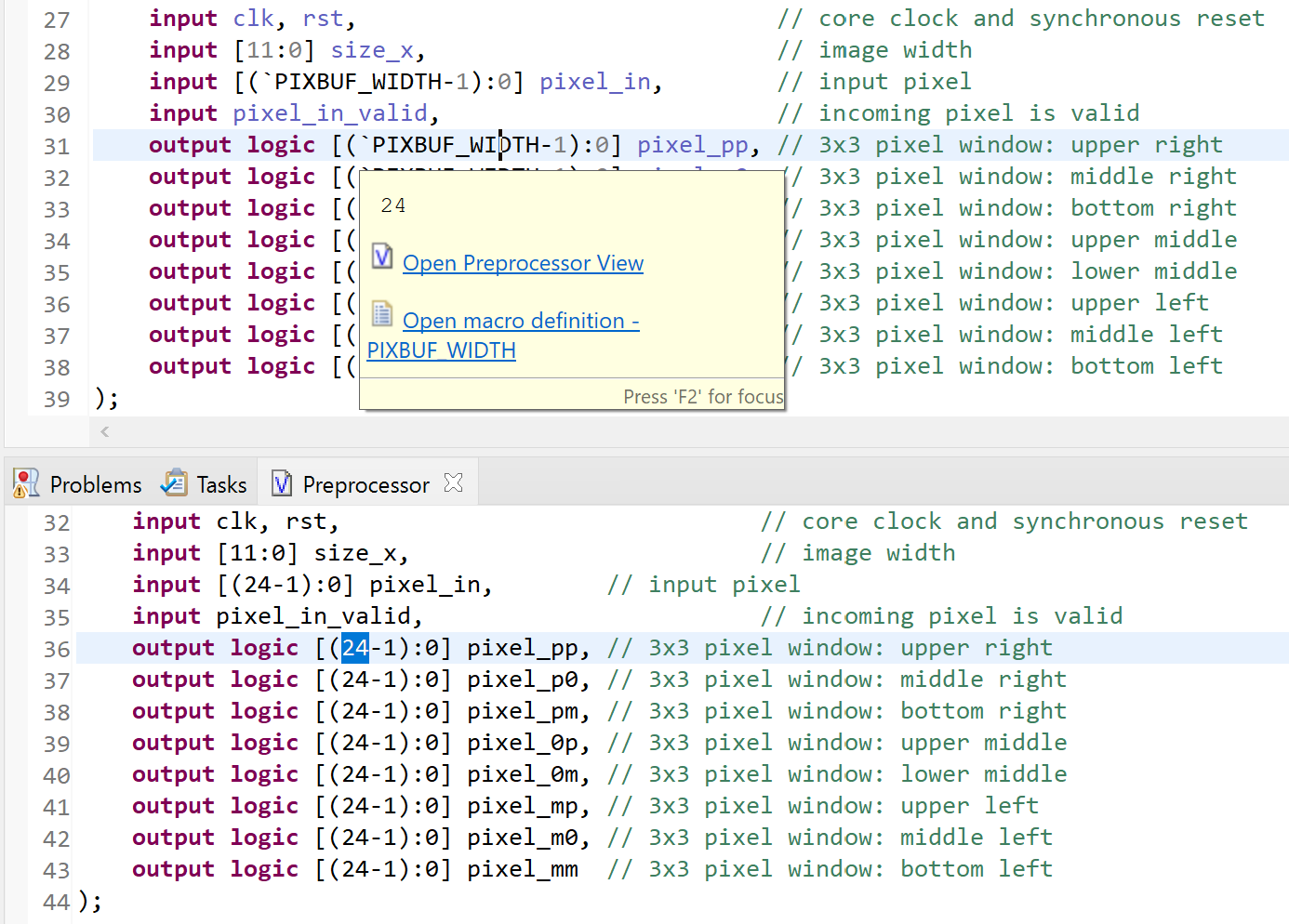
When you hover over a SystemVerilog preprocessor directive (e.g. include ...), SVH shows the preprocessed text.
You can find a convenient link to open the Preprocessor View at the bottom of this hover.
Ctrl+Click on `defines (or F3) will lead you to the corresponding declaration. Autocomplete will also offer you a list of all visible `defines.
In the Preprocessor View, you can preview the expanded version of your preprocessed SystemVerilog source files.